Housing affordability: practical ideas that can work in Romanian cities

Housing affordability remains a pressing issue for many residents in Romanian urban areas, where rising costs and limited supply have challenged access to adequate living spaces. Addressing this requires practical solutions tailored to local contexts and economic realities.
Current Challenges in Romanian Housing Markets
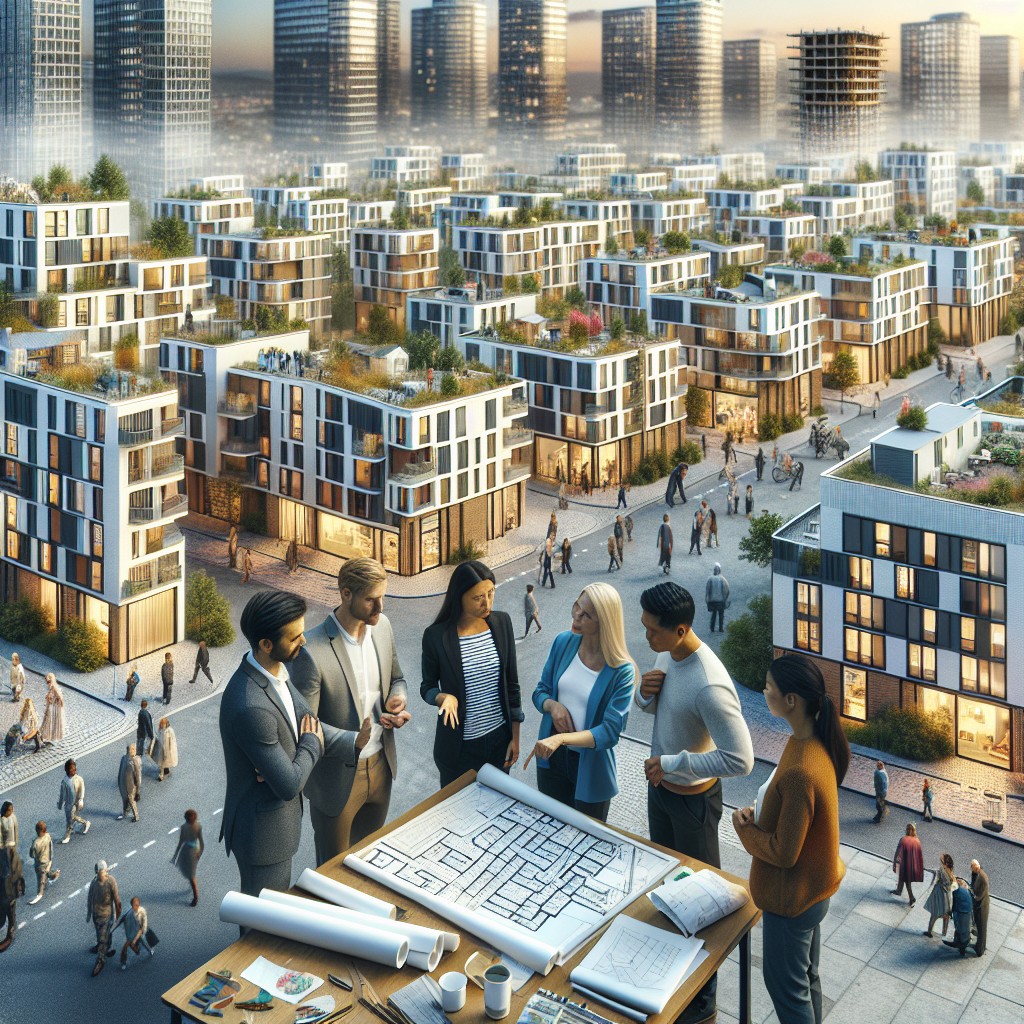
Romanian cities have experienced significant shifts in their housing landscapes over recent years, marked by increased demand and price volatility. Key factors influencing housing affordability include urbanization trends, wage stagnation, and a shortage of affordable new constructions. Many residents struggle to secure housing that balances cost, quality, and location, which affects social stability and economic growth.
Improving Public Housing Initiatives
Government-led public housing programs offer a direct approach to improving affordability. Enhancing these initiatives by increasing funding, streamlining bureaucratic procedures, and prioritizing sustainable construction can deliver more affordable units at scale. Incorporating community input in planning ensures that new developments meet residents’ needs, potentially reducing the housing shortage in cities like Bucharest, Cluj-Napoca, and Timisoara.
Promoting Affordable Housing Through Incentives
Introducing financial incentives for private developers can stimulate the construction of affordable housing options. Reduced taxes, subsidies, and relaxed zoning restrictions encourage investment without compromising urban planning standards. Furthermore, public-private partnerships have proven effective internationally by combining resources to expand the housing supply targeted at lower-income groups.
Utilizing Technology and Innovation in Construction
Advancements in construction technology offer promising pathways to reduce costs and construction times. Prefabricated building components and 3D printing methods can make housing development more efficient and affordable. Romanian cities can benefit by integrating these technologies into public and private housing projects, potentially lowering prices and improving quality.
Encouraging Sustainable Urban Development
Long-term housing affordability also depends on sustainable urban policies. Mixed-income neighborhoods, improved public transportation, and smart land use contribute to lowering housing costs and improving residents’ quality of life. Romanian municipalities investing in sustainable infrastructure are positioned to create more inclusive and affordable living environments.
Conclusion
Addressing housing affordability in Romanian cities demands a multifaceted strategy that combines public investment, private sector incentives, technological innovation, and sustainable planning. By adapting proven international practices within local contexts, Romania can improve access to affordable housing for its urban populations and foster more balanced urban development in the coming years.
Frequently Asked Questions about housing
What factors contribute to housing affordability issues in Romanian cities?
Key contributors include rising housing prices driven by demand, limited affordable housing supply, wage growth lagging behind costs, and urbanization pressures.
How can public housing improve housing affordability?
Public housing increases affordable options by providing subsidized or below-market-rate units, directly addressing shortages in urban centers.
Are private sector incentives effective in creating affordable housing?
Yes, financial incentives like tax breaks and subsidies can encourage developers to build housing that meets the needs of lower-income residents.
What role does technology play in making housing more affordable?
Innovative building technologies reduce construction costs and time, making it more feasible to produce affordable housing without sacrificing quality.
How does sustainable urban development impact housing affordability?
Sustainable development promotes efficient land use and better infrastructure, which can lower living costs and support long-term affordability in cities.